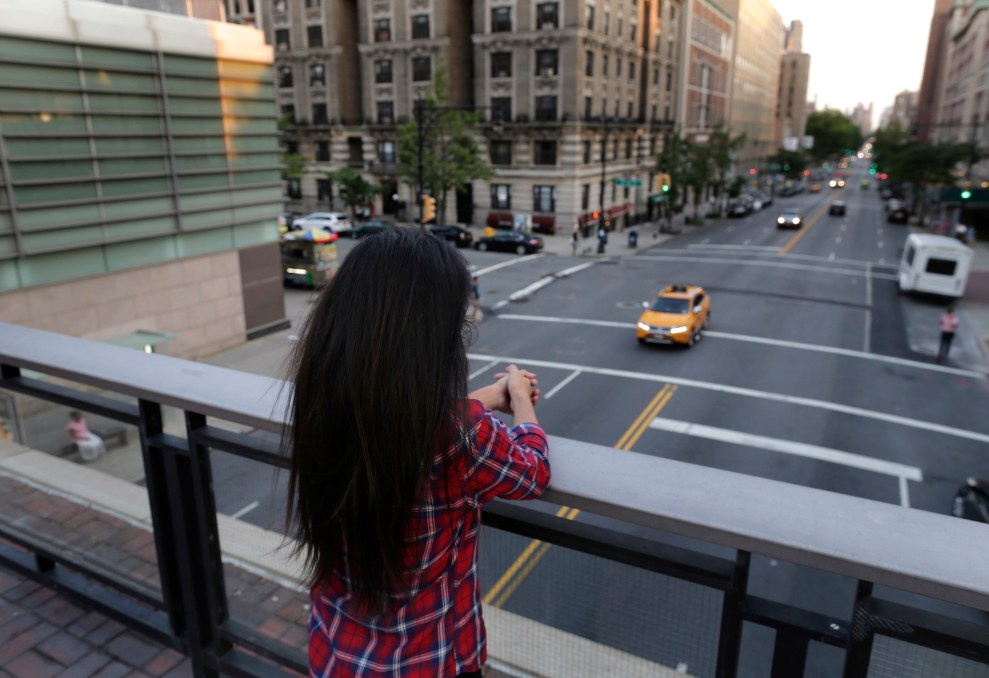
Another US Bohra woman who experienced female genital mutilation. Julie Jacobson/AP
Last week, an Indian American doctor was arrested in Michigan, charged with performing female genital cutting on two seven-year-old girls. As the story hit the local press and then the New York Times, and as it was shared by George Takei and Nicholas Kristof, my phone kept blowing up with breathless messages and links from childhood friends across the country.
“This story isn’t going away,” said one friend over the phone. We both grew up in the same controversial, secretive South Asian Muslim sect as the doctor, a 44-year-old emergency room physician named Jumana Nagarwala who was born in Washington, DC. “This time, the community can’t just pretend it’s not happening.” Just today, two more followers of the sect were arrested in connection with the case.
Our sect is known as the Dawoodi Bohras, a Shiite branch of Islam based in Gujarat, India, with an estimated 1.2 million followers around the world and thriving outposts across America. Some Bohras and others say the sect has veered toward a cult of personality and away from Islamic principles; it’s ruled by a well-heeled clergy of “totalitarian kings” with unusually wide-reaching control over their followers. (The Bohra clergy did not respond to Mother Jones‘ request for comment.)
Federal officials believe Nagarwala may have been clandestinely cutting girls since at least 2005. It’s the first case of its kind in the United States, where female genital cutting is a criminal sexual act and has been illegal since 1996. The practice is widely seen as an attempt to curb women’s sexuality by making sex less enjoyable, even painful.
Nagarwala admits she performed a procedure on the two seven-year-old girls, but says she didn’t cut them—she merely wiped away a mucous membrane and gave the gauze to the parents, who would bury it in keeping with Bohra tradition. She told investigators she’s not aware of anyone in her community who practices cutting.
As little girls, nearly all my female Bohra friends and I underwent khatna, the sect’s term for this practice. None of us remember being “wiped.” We were cut. Some of us bled and ached for days, and some walked away with lifelong physical damage. In interviews with investigators, one of the girls Nagarwala performed on said the procedure hurt so badly that she screamed in pain and “could barely walk afterward.” She drew a picture of the room where it happened, and marked an “X” to show where she bled on an exam table. Medical examinations show that both girls’ genitals have been altered.
While news coverage and the federal case focus on Nagarwala, khatna has been a mandatory religious practice inflicted on Bohra girls all over the world for generations, often in knowing violation of local laws. Bohras are the only Muslims in India who enforce female genital cutting; it’s not a common practice among South Asians or Muslims worldwide, and it’s not mentioned in the Koran. Privately, many Bohras have been praying for the clergy to end this practice for years, even decades. More than one mother I know wept when she learned she was bearing a girl, dreading what she might have to do to her child.
“Maybe this is the case that finally scares them into stopping it,” another friend messaged me. Her khatna happened during a family vacation in India. Mine took place in the bedroom of a family acquaintance in New Jersey in the late ’80s.
I buried the memory until I was 13, when my freshman year social-studies teacher put on a video about female genital mutilation in Africa. As I watched a young girl, dark-skinned like me, being prepared by village elders for her mutilation, I suddenly flashed back to a dim, chilly house my mother took me to when I was about seven. Two Indian aunties I had never seen before held me down on a mattress and pulled down my underwear as I squirmed to get free. One of them held a small pair of silver scissors, like the ones my dad used to keep his beard trimmed. Then, the sudden sensation of a tight, mean little pinch between my legs.
The memory exploded in my head in the dark, quiet classroom, and suddenly, a recurring nightmare I’d had for years made sense. In those dreams, the lower half of my body was made of kid’s construction toys, and pieces kept breaking off as I frantically tried to keep myself together. I began sobbing at my desk. The teacher kindly told me to catch my breath in the hallway; she thought I was upset over the images I was seeing in the video. Later, at lunch, my white girlfriends talked about being relieved that sort of thing doesn’t happen in America.
But it does. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that half a million girls in the United States were affected by or at risk for mutilation in 2012. I know of dozens of Bohra women whose parents had them cut in America over the last 30 years, from New York City to Houston to Chicago. Others were taken out of country to have the procedure done, a practice called “vacation cutting” that’s now also illegal in the United States.
We’re the first generation of Bohras born in America. Our parents began settling here after the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, which brought a wave of South Asian engineers, doctors, and other professionals to America. In our teens and 20s, my friends and I who underwent khatna assured each other the practice would die out as Bohras assimilated. We’re now in our 30s, and it hasn’t stopped. Some women our age and younger are still arranging or considering khatna for their own daughters.
“Nothing is going to change,” sighed the friend who called me to discuss the Nagarwala case. She spoke with a bitterness I could almost taste in my own mouth. “They’ll use this one doctor as a scapegoat, let her take the heat, and pretend it never happened.”
In 2015, the Australian Supreme Court handed down the first-ever conviction for a Bohra engaged in khatna. Many Bohras opposed to the practice hoped this was finally khatna‘s death knell. The Bohra clergy takes pains to maintain good relations with political leaders around the world; a guilty verdict in an affluent, English-speaking country seemed disastrous, especially in an increasing atmosphere of global Islamophobia.
Instead, the head cleric, Mufaddal Saifuddin, 70, seemed to double down on the practice during a cryptic sermon delivered last year in Mumbai. Congregations in the United States and elsewhere were sent letters instructing them to follow local laws, but some reading between the lines heard different instructions: Go underground, and don’t get caught. The parents in the Michigan case traveled with their daughters from Minnesota in February; community members tell me it’s become harder—but not impossible—to find Bohras willing to perform the procedure.
The task of getting a young girl’s khatna done falls on adult female relatives; men often don’t know it’s happening, or even that the practice exists at all. Girls are told to keep the procedure a secret after it’s performed, and they usually do. “For the longest time, I didn’t even know other people had this done, too,” one friend from the community told me. “I thought it was something my mom only did to me, and I didn’t know why.”
In the vacuum of secrecy, and with very little official guidance from Bohra leadership, there are wide variations in how khatna is performed. The seven-year-old girls in the Michigan case were allegedly cut by a licensed medical professional in an unnamed medical clinic. (Nagarwala’s employer, Henry Ford Hospital, says it did not happen on their grounds.) In other cases, the cutting is performed by laypeople with no medical training in unhygienic conditions.
There’s also little consensus about how the actual procedure is supposed to work; it’s often up to the interpretation of whoever is wielding the blade. In some cases, like mine, a “pinch of skin” from the clitoral hood is cut away, leaving no lasting physical trauma. Sometimes the entire clitoris is removed, or surrounding tissue is also damaged. Last year, writer Mariya Karimjee went on This American Life to tell the story of her cutting, which was performed in Pakistan and left her unable to have sex without unendurable pain.
Bohras even disagree on why khatna is performed. The prevailing view is that it keeps girls and women from becoming sexually promiscuous. Others say it has something to do with “removing bad germs” and liken it to male circumcision, which is widely (though not universally) believed to have hygienic benefits. The World Health Organization says female genital mutilation has no known health benefits and “violates the rights to health, security and physical integrity of the person, the right to be free from torture and cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment, and the right to life when the procedure results in death.”
Despite the prevalence of khatna among generations of Bohra women around the world, there has been almost no public conversation about it until just a few years ago. Speaking out about any of the numerous issues the clergy has come under scrutiny for—khatna, multiple lawsuits over alleged abuses of power, “big brother”-style surveillance of everyday Bohras—is seen as unacceptable. Dissidents can face excommunication and social boycott. The threat extends to family members, whose businesses often depend on Bohra financing, or who may not be allowed to marry within the community or be buried in a Bohra cemetery unless the rebellious relative is quieted.
I’m already estranged from my family because of disagreements over Bohra customs. Like a few of my friends, I’ve tried to bring up khatna to my parents, mostly my mother, with little progress. As in many rigid orthodoxies, the burden of social policing in the Bohra community falls largely on women, who have the most to lose from rocking the boat and who are often suffering from unacknowledged personal trauma of their own.
That’s why it’s remarkable that so many Bohra women have started speaking up over the last few years, from the explosive This American Life story to a documentary film, interviews with major news outlets in India and the United States, and a Change.org petition calling on the Bohra clergy to end the practice that’s been signed by 150,000 supporters. In 2015, five young women started a Bohra anti-FGM group called Sahiyo (Gujarati for “friends”) and conducted the first large-scale, global research study on the practice of khatna among Dawoodi Bohras. Nearly 400 Bohra women took the online survey, mostly from India and the United States and between the ages of 18 and 45. Eighty percent said they would like the practice of khatna to end.
None of this has moved the clergy to unequivocally end it.
One of the girls in the Nagarwala case in Michigan was temporarily taken away from her parents, an act that’s sure to cause additional trauma. Nagarwala could be sentenced anywhere from five years to life in prison for the assortment of charges she faces, though she’s just one of an untold number of khatna practitioners around the country. Bohras opposed to the practice now find themselves rooting against those who are arguably fellow victims.
“It feels sick to be happy about all this punishment,” said one of my friends the other night. “But I just don’t know how else to make them listen.”