Image by Shutterstock
Last year, the Food and Drug Administration proposed a set of voluntary “guidelines” designed to nudge the meat industry to curb its antibiotics habit. Ever since, the agency has been mulling whether and how to implement the new program. Meanwhile, the meat industry has been merrily gorging away on antibiotics—and churning out meat rife with antibiotic-resistant pathogens—if the latest data from the FDA itself is any indication.
The Pew Charitable Trusts crunched the agency’s numbers on antibiotic use on livestock farms and compared them to data on human use of antibiotics to treat illness, and mashed it all into an infographic, which I’ve excerpted below. Note that that while human antibiotic use has leveled off at below 8 billion pounds annually, livestock farms have been sucking in more and more of the drugs each year—and consumption reached a record nearly 29.9 billion pounds in 2011. To put it another way, the livestock industry is now consuming nearly four-fifths of the antibiotics used in the US, and its appetite for them is growing.
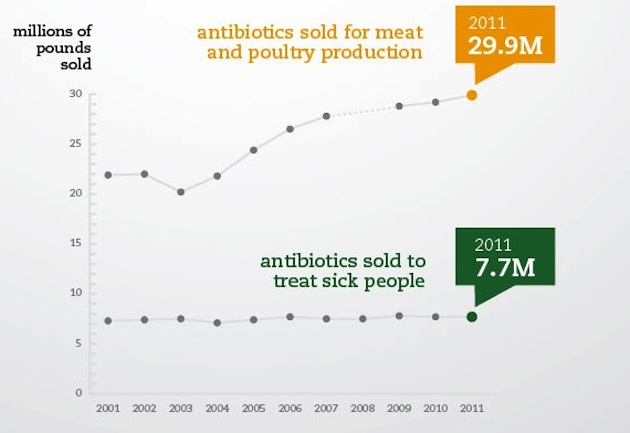
In an email, a Pew spokesperson added that while the American Meat Institute reported a 0.2 percent increase in total meat and poultry production in 2011 compared to the previous year, the FDA data show that antibiotic consumption jumped 2 percent over the same time period. That suggests that meat production might be getting more antibiotic-intensive.
Not surprisingly, when you cram animals together by the thousands and dose them daily with antibiotics, the bacteria that live on and in the animals adapt and develop resistance to those bacteria killers. Pew crunched another new set of data, the FDA’s latest release of results from its National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System, or NARMS, which buys samples of meat products and subjects them to testing for bacterial pathogens. Again, the results are sobering. Here a a few highlights pointed to by Pew in an email:
• Of the Salmonella on ground turkey, about 78% were resistant to at least one antibiotic and half of the bacteria were resistant to three or more. These figures are up compared to 2010.
• Nearly three-quarters of the Salmonella found on retail chicken breast were resistant to at least one antibiotic. About 12% of retail chicken breast and ground turkey samples were contaminated with Salmonella.
• Resistance to tetracycline [an antibiotic] is up among Campylobacter on retail chicken. About 95% of chicken products were contaminated with Campylobacter, and nearly half of those bacteria were resistant to tetracyclines. This reflects an increase over last year and 2002.
Takeaway: While the FDA dithers with voluntary approaches to regulation, the meat industry is feasting on antibiotics and sending out product tainted with antibiotic-resistant bugs.

















