<a href="http://www.shutterstock.com/pic-152853110/stock-photo-successful-man-raising-arms-after-cross-track-running-on-summer-sunset-fitness-male-athlete-with.html?src=BZ06znTUSE1DSYgrClfA-A-1-17">Dirima</a>/Shutterstock
The only way to stop climate change is to drastically reduce, and ultimately eliminate, greenhouse gas emissions. If you want to know how well we’re doing on that goal, a good place to start is the Environmental Protection Agency’s official GHG database. And frankly, the picture isn’t very pretty.
The total level of US emissions in 2014 wasn’t very different than it was 30 years ago:
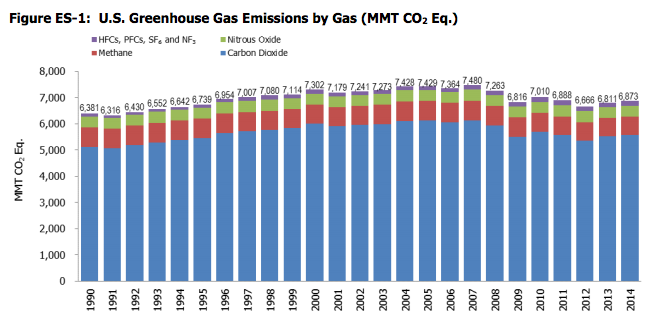
However, total emissions is a fairly misleading way to look at progress on climate change. Most of these emissions come from fossil fuels burned to make energy—either electricity from power plants or gas for cars and trucks. So emissions are heavily influenced by economic activity; a downturn in the economy would mean people drive less, factories use less electricity, etc., and the outcome would be lower emissions. At least, that’s the way things used to be.
Over the last few years, the United States and many other countries around the world have seen an unprecedented disconnect between gross domestic product and emissions. Thanks to an increasingly large share of energy coming from renewables and vast improvements to energy efficiency, emissions can now be increasingly “decoupled” from economic activity. In other words, it’s now possible to grow the economy without growing emissions.
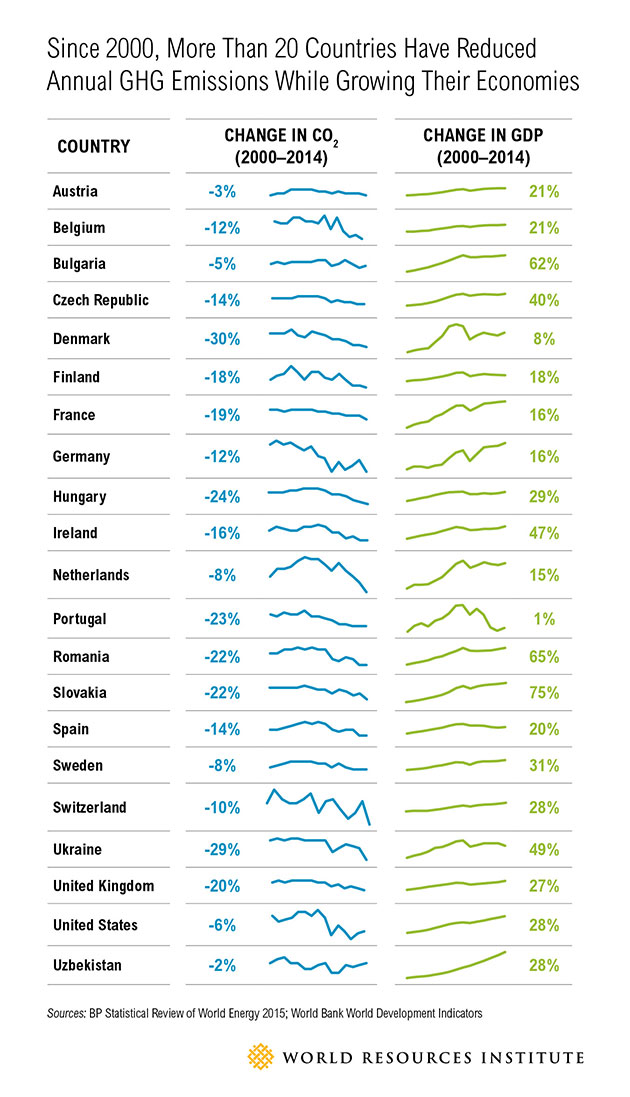
A new analysis from the World Resources Institute illustrates how this trend is already playing out around the world. It’s a bit of good news, and a solid rebuttal to anyone who says saving the climate means killing the economy—looking at you, Donald Trump: