Last week I linked to a report showing a sharp increase in rates for treasury bonds that mature in late October. This is a signal that markets are starting to get genuinely nervous about the possibility of delayed payment on these notes. Today, Neil Irwin passes along the latest on this. As the chart on the right shows, the rates on short-term bills 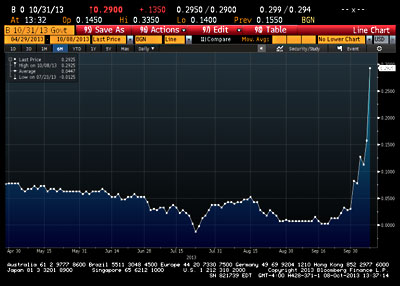 have hovered right around zero percent for all of September. Then, starting October 1, rates started to rise. In the past 48 hours, they’ve spiked enormously:
have hovered right around zero percent for all of September. Then, starting October 1, rates started to rise. In the past 48 hours, they’ve spiked enormously:
There are reports, including this one from Reuters, indicating that some of the biggest money managers in the world are starting to avoid U.S. government debt that matures in the near future out of fear they will not be repaid promptly. Bond investors seem to be confident that the U.S. government will make good on its obligations in the longer term –securities that mature a year or more from now are actually seeing their rates fall. But they are becoming less confident that these short-term securities will pay on time.
Ironically, this can create self-fulfilling problems for the Treasury. Treasury bills roll over every week, on Thursdays. Here’s how it works: The government issues the bills for a “discount,” then refunds the par value when they come due. So, for example, an investor might pay $995 for a bill that returns $1,000 in three months, for an equivalent of about a 2 percent annual interest rate.
As Irwin says, there’s an easy answer to this. Just raise the debt ceiling.