Derailed oil tanker train cars burn near Mount Carbon, W.Va., on Monday.The Daily Mail, Marcus Constantino/AP
A train hauling more than 100 tankers from North Dakota’s booming oil fields derailed during a snowstorm on Monday in West Virginia. The accident sparked massive explosions that prompted the evacuation of two nearby towns, and an oil spill that threatened the water supply of thousands of local residents. The train was heading to Yorktown, Virginia, and came off its tracks 33 miles southeast of Charleston, West Virginia. A state of emergency was declared.
Oil spilled into the Kanawha River, and one home was destroyed during the inferno that continued for 10 hours after the derailment, according to CNN. One person was injured. Dramatic footage shows fire and smoke billowing through the snowy sky:
Another explosion just happened here at the train derailment: pic.twitter.com/ZqoSCVRoAH
— Matt Heckel (@WSAZmattheckel) February 17, 2015
Bakken crude is regarded as potentially more flammable than traditional crude, thus posing an increased hazard. And since the derailment of a train hauling Bakken crude killed 47 people in Lac-Mégantic, Quebec, in July 2013, the type of tankers involved in these accidents has become the subject of intense scrutiny. Both Canada and the United States have called for tougher safety standards, including upgrading the tankers. In mid-January, Canada announced it would take older tankers, known as the “DOT-111”, off the network years sooner than the United States will, putting the two countries at odds over increased safety measures on the deeply integrated system.
Here’s a diagram of the weaknesses in the older DOT-111 model tanker, which is still in operation across the network:
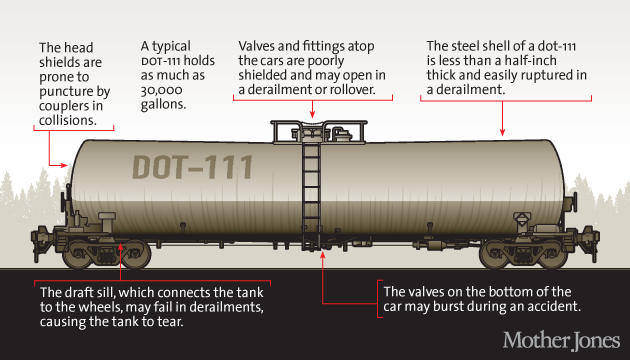
You can read an in-depth Mother Jones report about the DOT-111 tankers here.
The train operator, CSX, has said that the train was not pulling DOT-111 tankers. Instead, the company says it was using a tougher, newer model, the “CPC 1232”, according to Reuters.
But even newer cars like these are evidently not invincible: when a 105-car CSX train derailed in Lynchburg, Va., last April, a fiery CPC-1232 tanker careened into the James River and spilled 30,000 gallons of Bakken crude oil. And Washington state regulators are investigating CPC-1232 tankers, after a BNSF train carrying Bakken crude oil across Idaho and Washington in January was found to have leaking cars. The CPC-1232 also doesn’t quite live up to the US regulators’ proposed rules to upgrade the system, according to Bloomberg, which reports that:
The draft rule also would require that new cars be built with steel shells that are 9/16th of an inch thick, people familiar with the plan said. The walls of the current cars, both DOT-111s and the newer CPC-1232 models, are 7/16th of an inch thick.
The West Virginia accident on Monday is the second major derailment in three days across North America’s booming oil-by-rail network. A Canadian National Railway train detailed northern Ontario, Canada, on Saturday night, again resulting in an inferno and an oil spill: 29 railway cars in the 100-car train derailed. Seven caught fire, according to CTV.















