<a href="http://www.shutterstock.com/pic-193998131/stock-photo-a-pair-of-female-feet-standing-on-a-bathroom-scale.html?src=S9Rx0NSBJgetjIuPZfT0NA-1-17">Sedlacek</a>/Shutterstock
Bulging waistlines have become the new normal in the United States, according to Monday’s “State of Obesity” report. Though only five states saw increases in adult obesity last year, researchers noted little improvement to the nation’s weight crisis overall: The average American adult is 24 pounds heavier than in 1980, when obesity rates were less than half of their present levels. The report is published annually by Trust for America’s Health and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
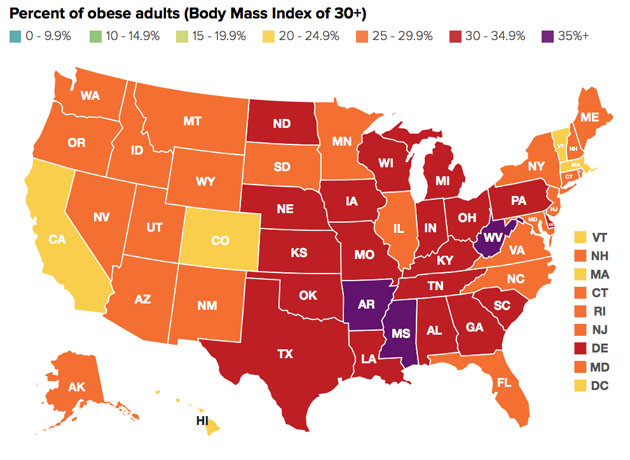
With more than one-third of Americans considered obese and nearly 70 percent of them overweight, rates of obesity-linked diseases have also risen steadily. Across the South and the Midwest, where the obesity crisis is most severe (Arkansas, West Virginia, and Mississippi topped the scales in this year’s report), rates of hypertension and diabetes climbed past record highs. Racial and economic disparities are also acute: Nearly half of black adults are now obese, compared with just under one-third of white adults. The researchers said higher rates of food insecurity, targeted marketing of unhealthy foods, and unequal health care access were all factors contributing to the disparity.
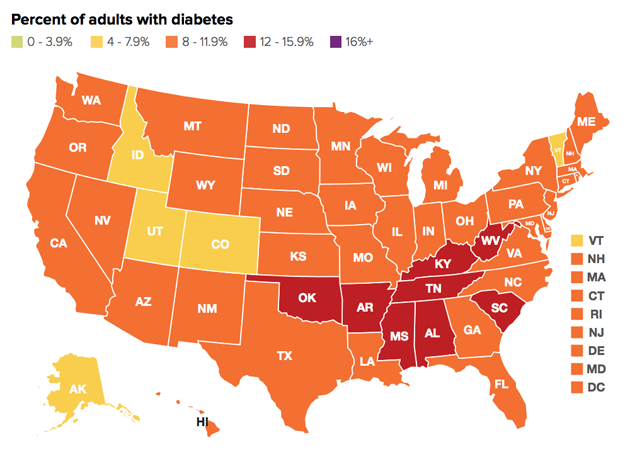
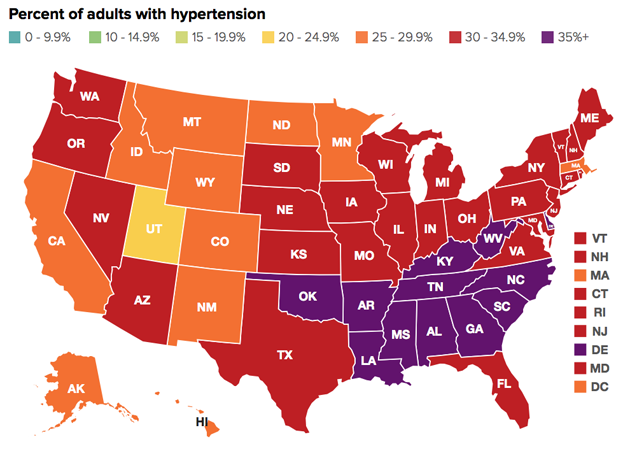
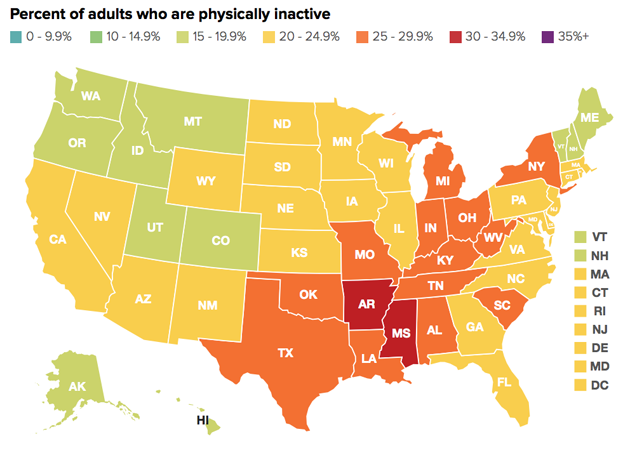
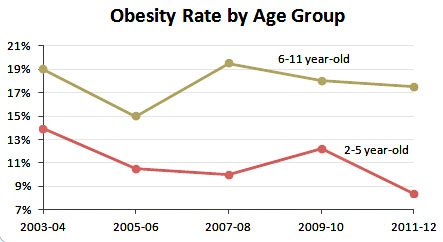
But the researchers also note a few areas where policy and lifestyle have curbed crisis-level rates. Obesity was less of an issue in states out West and in the Northeast, where sedentary lifestyles are less common. (The nation’s slimmest state, Colorado, also had the lowest rate of physical inactivity). And while the child obesity rate remains three times its level from 1980, the researchers add that outreach to parents, programs offering nutrition assistance, and healthy-eating campaigns in schools seem to be making a difference: Obesity among children has declined since 2004.