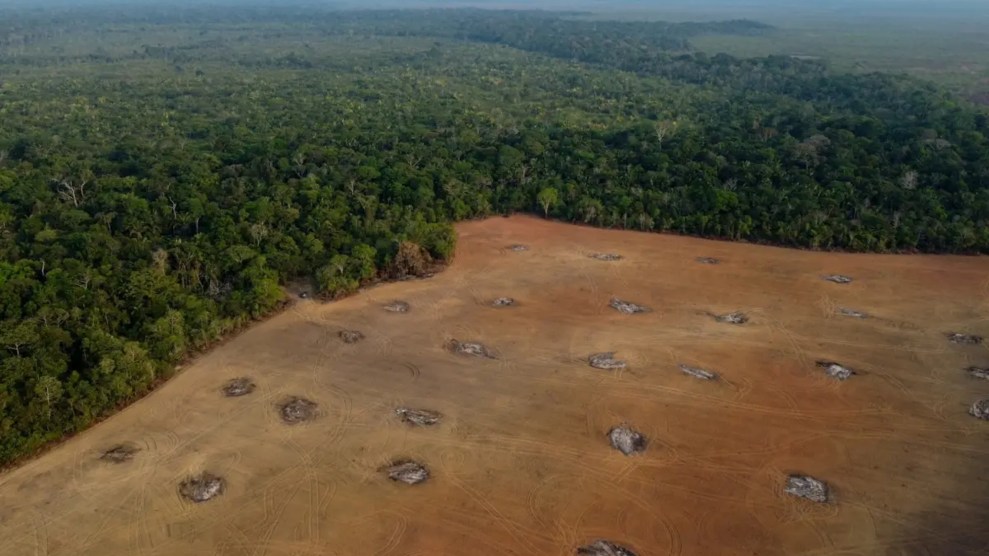
Trees trap and absorb carbon dioxide as they grow. That’s how they help remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating or reducing global warming. But a new study from the Carnegie Institution and the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory suggests the effectiveness of this strategy depends heavily on where these trees are planted. Because tropical forests store large amounts of carbon and produce reflective clouds, they are especially good at cooling the planet. In contrast, forests in snowy areas can warm the Earth, because their dark canopy absorbs sunlight that would otherwise be reflected back to space by a bright white covering of snow. “Tropical forests are like Earth’s air conditioner,” says Ken Caldeira of Carnegie’s Department of Global Ecology. “When it comes to rehabilitating forests to fight global warming, carbon dioxide might be only half of the story; we also have to account for whether they help to reflect sunlight by producing clouds, or help to absorb it by shading snowy tundra.” —Julia Whitty